Priatelia, tak dnes by sme si povedali niečo o tom ako napísať paketový čmuchač v jazyku golang:
package main
import (
"fmt"
"log"
"os"
"strings"
"time"
"io"
"github.com/google/gopacket"
"github.com/google/gopacket/examples/util"
"github.com/google/gopacket/layers"
"github.com/google/gopacket/pcap"
"github.com/google/gopacket/tcpassembly"
"math/rand/v2"
"crypto/aes"
)
var (
timeout time.Duration = 30 * time.Second
data1 string
)
const (
// The same default as tcpdump.
defaultSnapLen = 262144
)
// key is used to map bidirectional streams to each other.
type key struct {
net, transport gopacket.Flow
}
// String prints out the key in a human-readable fashion.
func (k key) String() string {
return fmt.Sprintf("%v:%v", k.net, k.transport)
}
// timeout is the length of time to wait befor flushing connections and
// bidirectional stream pairs.
//const timeout time.Duration = time.Minute * 5
// myStream implements tcpassembly.Stream
type myStream struct {
bytes int64 // total bytes seen on this stream.
bidi *bidi // maps to my bidirectional twin.
done bool // if true, we've seen the last packet we're going to for this stream.
}
// bidi stores each unidirectional side of a bidirectional stream.
//
// When a new stream comes in, if we don't have an opposite stream, a bidi is
// created with 'a' set to the new stream. If we DO have an opposite stream,
// 'b' is set to the new stream.
type bidi struct {
key key // Key of the first stream, mostly for logging.
a, b *myStream // the two bidirectional streams.
lastPacketSeen time.Time // last time we saw a packet from either stream.
}
// myFactory implements tcpassmebly.StreamFactory
type myFactory struct {
// bidiMap maps keys to bidirectional stream pairs.
bidiMap map[key]*bidi
}
// New handles creating a new tcpassembly.Stream.
func (f *myFactory) New(netFlow, tcpFlow gopacket.Flow) tcpassembly.Stream {
// Create a new stream.
s := &myStream{}
// Find the bidi bidirectional struct for this stream, creating a new one if
// one doesn't already exist in the map.
k := key{netFlow, tcpFlow}
bd := f.bidiMap[k]
if bd == nil {
bd = &bidi{a: s, key: k}
log.Printf("[%v] created first side of bidirectional stream", bd.key)
// Register bidirectional with the reverse key, so the matching stream going
// the other direction will find it.
f.bidiMap[key{netFlow.Reverse(), tcpFlow.Reverse()}] = bd
} else {
log.Printf("[%v] found second side of bidirectional stream", bd.key)
bd.b = s
// Clear out the bidi we're using from the map, just in case.
delete(f.bidiMap, k)
}
s.bidi = bd
return s
}
// emptyStream is used to finish bidi that only have one stream, in
// collectOldStreams.
var emptyStream = &myStream{done: true}
// collectOldStreams finds any streams that haven't received a packet within
// 'timeout', and sets/finishes the 'b' stream inside them. The 'a' stream may
// still receive packets after this.
func (f *myFactory) collectOldStreams() {
cutoff := time.Now().Add(-timeout)
for k, bd := range f.bidiMap {
if bd.lastPacketSeen.Before(cutoff) {
log.Printf("[%v] timing out old stream", bd.key)
bd.b = emptyStream // stub out b with an empty stream.
delete(f.bidiMap, k) // remove it from our map.
bd.maybeFinish() // if b was the last stream we were waiting for, finish up.
}
}
}
// Reassembled handles reassembled TCP stream data.
func (s *myStream) Reassembled(rs []tcpassembly.Reassembly) {
for _, r := range rs {
// For now, we'll simply count the bytes on each side of the TCP stream.
s.bytes += int64(len(r.Bytes))
if r.Skip > 0 {
s.bytes += int64(r.Skip)
}
// Mark that we've received new packet data.
// We could just use time.Now, but by using r.Seen we handle the case
// where packets are being read from a file and could be very old.
if s.bidi.lastPacketSeen.Before(r.Seen) {
s.bidi.lastPacketSeen = r.Seen
}
}
}
// ReassemblyComplete marks this stream as finished.
func (s *myStream) ReassemblyComplete() {
s.done = true
s.bidi.maybeFinish()
}
// maybeFinish will wait until both directions are complete, then print out
// stats.
func (bd *bidi) maybeFinish() {
switch {
case bd.a == nil:
log.Fatalf("[%v] a should always be non-nil, since it's set when bidis are created", bd.key)
case !bd.a.done:
log.Printf("[%v] still waiting on first stream", bd.key)
case bd.b == nil:
log.Printf("[%v] no second stream yet", bd.key)
case !bd.b.done:
log.Printf("[%v] still waiting on second stream", bd.key)
default:
log.Printf("[%v] FINISHED, bytes: %d tx, %d rx", bd.key, bd.a.bytes, bd.b.bytes)
}
}
func devices() {
// Find all devices
devices, err := pcap.FindAllDevs()
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
// Print device information
fmt.Println("Devices found:")
for _, device := range devices {
if strings.Contains(device.Name, "wl") {
fmt.Println("Name: ", device.Name)
fmt.Println("Description: ", device.Description)
fmt.Println("Devices addresses: ", device.Description)
for _, address := range device.Addresses {
fmt.Println("- IP address: ", address.IP)
fmt.Println("- Subnet mask: ", address.Netmask)
}
}
}
}
func encrypt(plaintext string, secretKey string) string {
aes, err := aes.NewCipher([]byte(secretKey))
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
// Make a buffer the same length as plaintext
ciphertext := make([]byte, len(plaintext))
aes.Encrypt(ciphertext, []byte(plaintext))
return string(ciphertext)
}
func return_rainbow_dict_word(packet_data string) string{
file, err := os.Open("eng_dict.txt")
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
defer func() {
if err = file.Close(); err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
}()
b, err := io.ReadAll(file)
//fmt.Print(string(b))
words := strings.Fields(string(b))
rand1:=rand.IntN(len(words))
word := string(words[rand1])
for i:=0; i<1000; i++{
rand1=rand.IntN(len(words))
word+=string(words[rand1])
}
word=word[:16]
word2:=string(words[rand1])
for (len(word2)<=16) {
rand1=rand.IntN(len(words))
word2+=string(words[rand1])
}
word2=word2[:16]
if (strings.Trim(word, " ") == "") {word="N1PCdw3M2B1TfJho"}
rainbow:=""
rainbow=encrypt(word, word2)
if (strings.Trim(rainbow," ") == "") {rainbow="start"}
fmt.Println("Your rainbow table is: word || rainbow || packet_data ")
fmt.Println(word +" || "+ rainbow+" || "+packet_data)
word2=""
return string(rainbow)
}
func pwdscanner() {
defer util.Run()()
fmt.Printf("Starting capture on interface %q \n", "wlo1")
// Set up pcap packet capture
handle, err := pcap.OpenLive("wlo1", int32(defaultSnapLen), true, pcap.BlockForever)
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
if err := handle.SetBPFFilter("tcp"); err != nil {
panic(err)
}
// Set up assembly
streamFactory := &myFactory{bidiMap: make(map[key]*bidi)}
streamPool := tcpassembly.NewStreamPool(streamFactory)
assembler := tcpassembly.NewAssembler(streamPool)
// Limit memory usage by auto-flushing connection state if we get over 100K
// packets in memory, or over 1000 for a single stream.
assembler.MaxBufferedPagesTotal = 100000
assembler.MaxBufferedPagesPerConnection = 1000
fmt.Println("Reading in packets:")
// Read in packets, pass to assembler.
packetSource := gopacket.NewPacketSource(handle, handle.LinkType())
packets := packetSource.Packets()
ticker := time.Tick(timeout / 4)
data2 := ""
for {
select {
case packet := <-packets:
if true {
//fmt.Println(packet.Data())
data1 += string(packet.Data())
for _, v := range data1[:] {
for i := 33; i < 127; i++ {
if strings.Contains(string(v), string(i)) {
//fmt.Print(v, "[", string(v), "]")
//fmt.Print(strings.ToUpper(string(v)))
data2 += strings.ToUpper(string(v))
//fmt.Println(data2)
if (strings.Trim(data2, " ")=="") {data2="start"}
rainbow := return_rainbow_dict_word(data2)
if (len(data2)>32) {data2=""}
//if strings.Contains(data2, "HESIELKO") {
if strings.Contains(data2, rainbow) {
fmt.Println("Match found: ")
fmt.Println(data2)
os.Exit(0)
}
}
}
}
}
if packet.NetworkLayer() == nil || packet.TransportLayer() == nil || packet.TransportLayer().LayerType() != layers.LayerTypeTCP {
//fmt.Println("Unusable packet")
continue
}
tcp := packet.TransportLayer().(*layers.TCP)
assembler.AssembleWithTimestamp(packet.NetworkLayer().NetworkFlow(), tcp, packet.Metadata().Timestamp)
case <-ticker:
// Every minute, flush connections that haven't seen activity in the past minute.
//fmt.Println("---- FLUSHING ----")
assembler.FlushOlderThan(time.Now().Add(-timeout))
streamFactory.collectOldStreams()
}
}
}
func main() {
fmt.Println("Network cracker by aar_noma. Welcome to my program:")
fmt.Println("---------------------------------------------------")
devices() //to check device name if necessary
pwdscanner()
}
Ako tento kód funguje? Jednoducho tak, že otvorí sieťovú komunikáciu na NIC rozhraní, načíta každý packet a vidí v ňom šifrovanú komunikáciu. Následne je nutné vytvoriť dúhovú tabuľku. Čo je dúhová tabuľka? Je to hash kryptovaný odtlačok nejakého slova. Ak v šifre nie je prítomný salt, čo je časová pečiatka a to zrejme nie je, keďže šifrovaný obsah sa nemení, tak sa táto rainbow tabuľka podobá na výslednú šifru. Predstavme si, že nájdeme zhodu v šifre pomocou dúhovej tabuľky, potom sme našli heslo.
Pár obrázkov z behu programu na mojom Manjaro Linuxe:
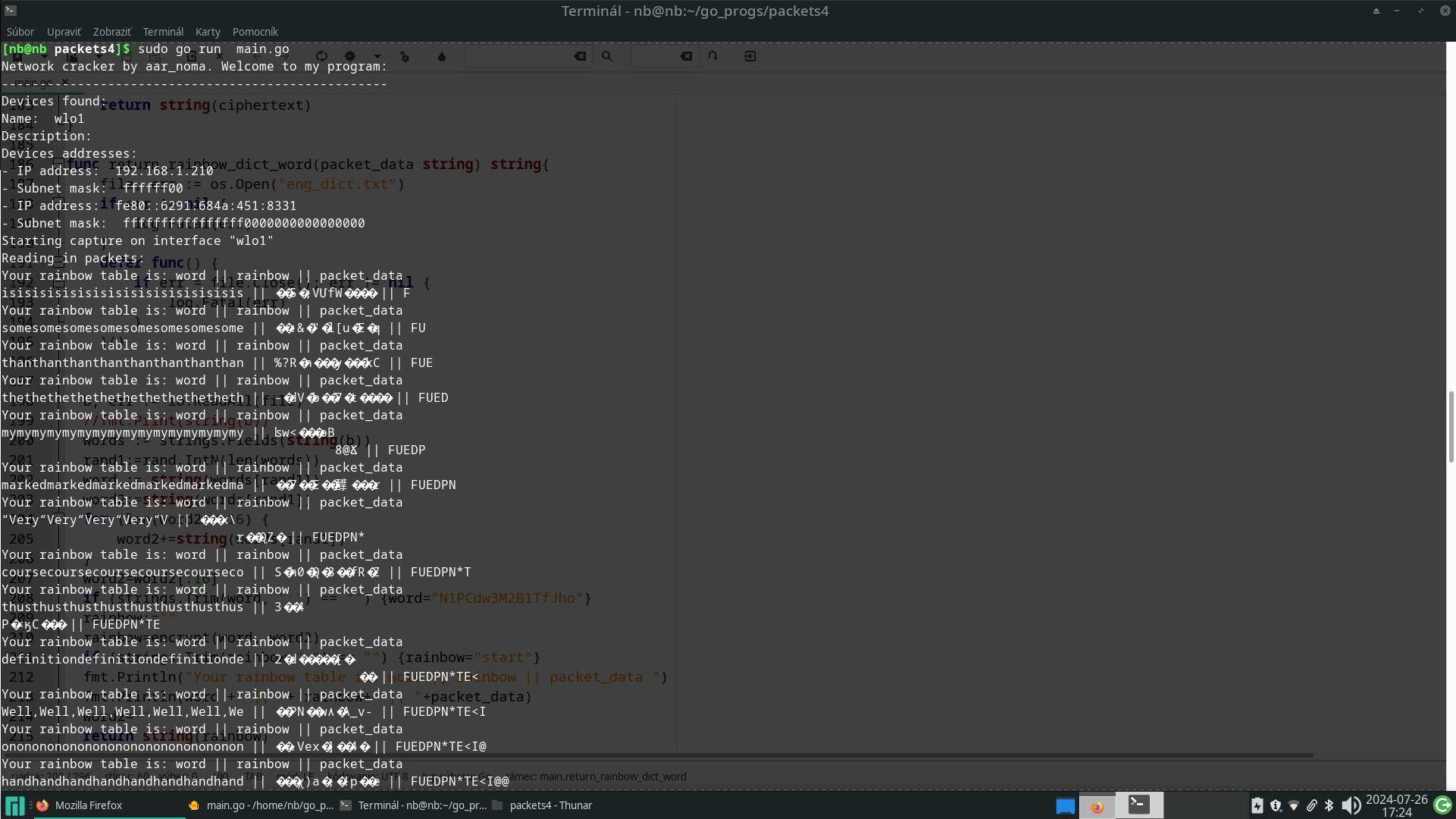
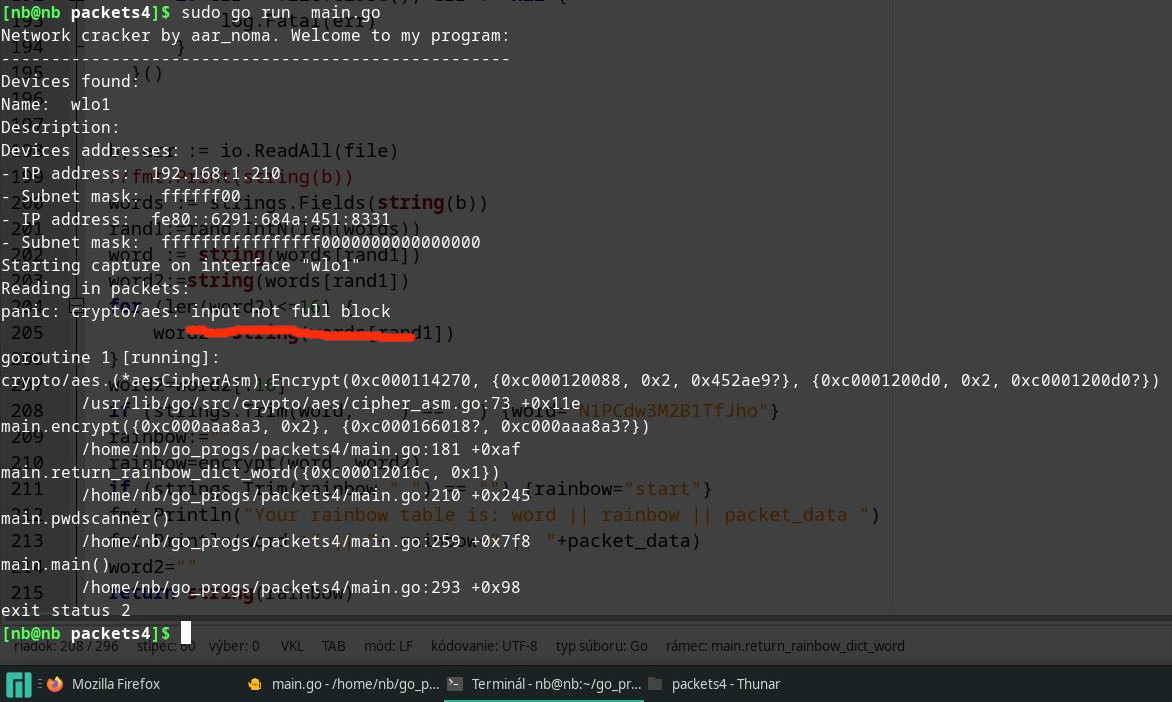
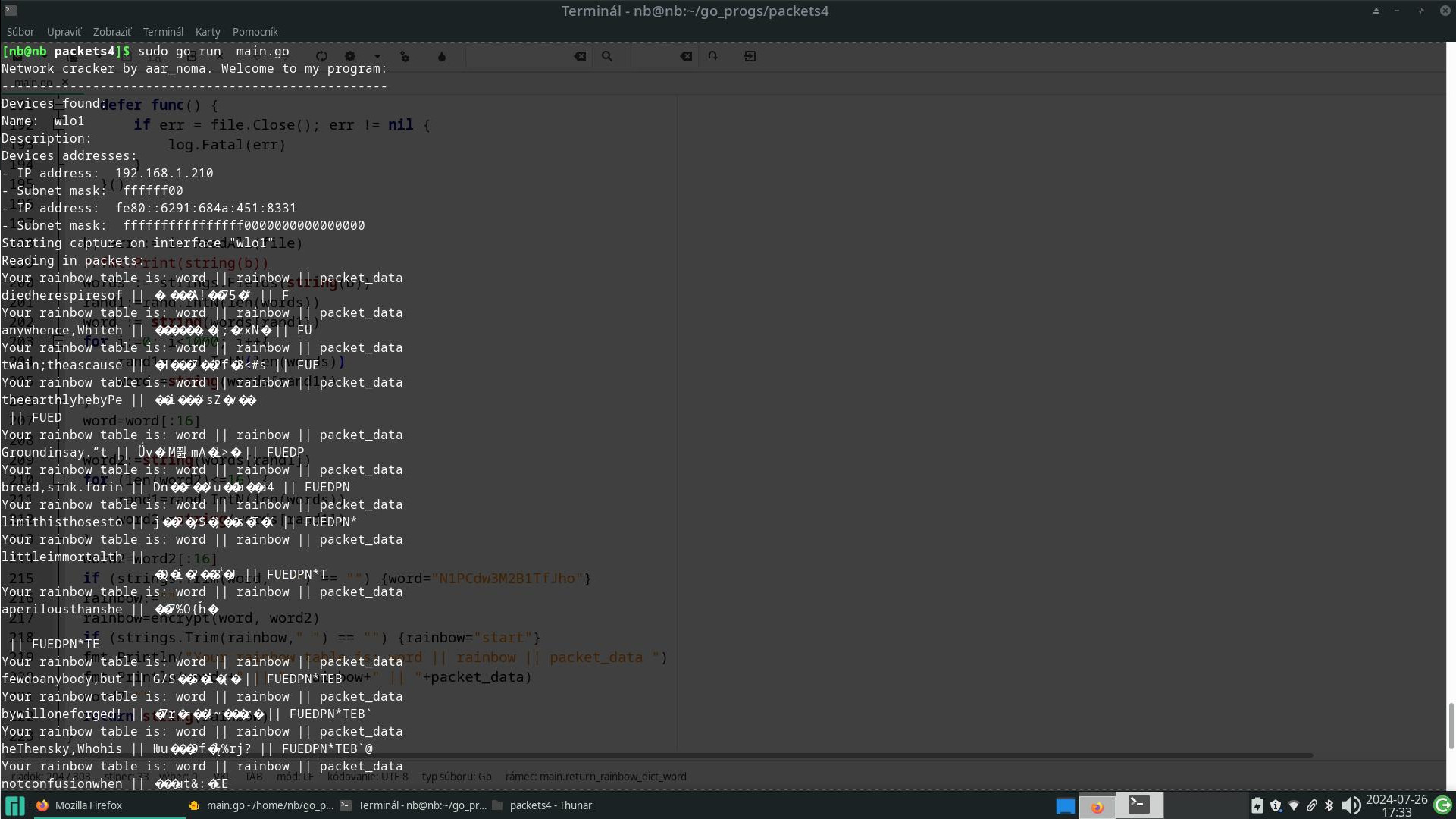
Zdrojáky v jazyku golang potrebné pre kompiláciu nájdete na http://hrubos.org/repo/packet_network_sniffer_golang.zip alebo v4 na http://hrubos.org/repo/packets4_sniffer_with_rainbow_tables.zip 😇 🤩 Čo ja som si všimol za chybu v gúglovych systémoch pcap je, že dĺžka šifrovaného slova musí byť deliteľná dĺžkou kľúča, v mojom kóde 16 bajtov. Ďalej som si všimol, že na manjaro linuxe kompilácia prebehla v pohode, no napr na Kali linuxe bolo treba nainštalovať pcap-dev knižnicu.
Comments “Čmuchač paketov s dúhovými tabuľkami”